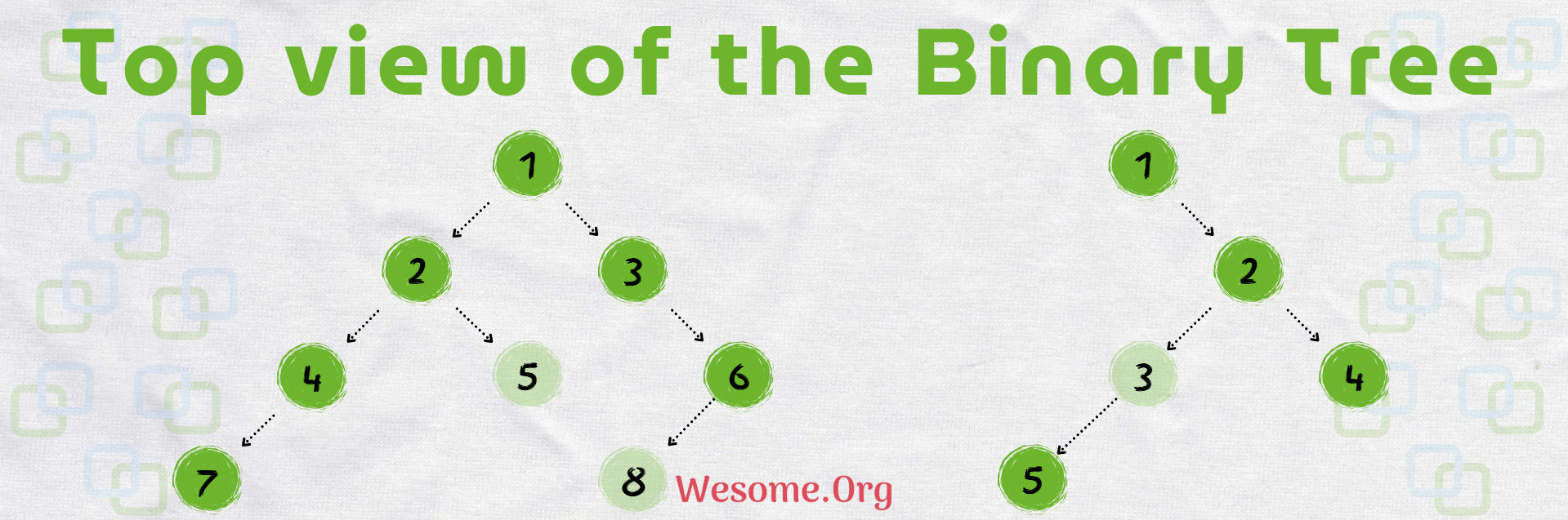
The top View of a Binary Tree displays the nodes that would be visible if you looked at the tree from directly above. This includes the leftmost and rightmost nodes at each horizontal level.
Code Flow for Print Top View of Binary Tree
-
Start:
-
Input the root node of the binary tree.
-
-
Check if the root is
null:-
If
true, terminate the process. -
If
false, proceed to the next step.
-
-
Create a TreeMap to store the top view (
map).-
Keys: Horizontal distances (
hrzDis). -
Values: Node values.
-
-
Create a Queue for level-order traversal and add the root node with
hrzDis = 0. -
While the queue is not empty:
-
Dequeue a node (
polloperation). -
Retrieve its horizontal distance (
hrzDis).
-
-
Check if the horizontal distance (
hrzDis) exists in theTreeMap:-
If not, add the node's data to the map (
map.put(hrzDis, data)).
-
-
Add the left child to the queue with
hrzDis - 1(if non-null). -
Add the right child to the queue with
hrzDis + 1(if non-null).
Let's see the code now
package org.wesome.dsalgo;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class BinarySearchTree {
Node root;
public static void topView(Node root) {
/* If the root node is null, the method returns immediately. */
if (Objects.isNull(root)) {
System.out.println("the root is null");
return;
}
/* Set the horizontal distance of the root node to 0. */
int hrzDis = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
// create a queue for level order traversal
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// Assign initialized horizontal distance value to root node and add it to the queue.
root.hrzDis = hrzDis;
// add root with level 0
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node tnode = queue.poll();
hrzDis = tnode.hrzDis;
// check if this is the first node for this level
if (!map.containsKey(hrzDis)) {
map.put(hrzDis, tnode.data);
}
// add left child in the queue with horizontal distance hrzDis-1.
if (Objects.nonNull(tnode.left)) {
tnode.left.hrzDis = hrzDis - 1;
queue.add(tnode.left);
}
// add right child in the queue with horizontal distance hrzDis+1.
if (Objects.nonNull(tnode.right)) {
tnode.right.hrzDis = hrzDis + 1;
queue.add(tnode.right);
}
}
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.print(entry.getValue() + " ");
}
}
void insert(int data) {
System.out.println("BinarySearchTree.insert data = " + data);
root = insert(root, data);
}
Node insert(Node root, int data) {
if (Objects.isNull(root)) {
Node tempNode = new Node(data);
return tempNode;
}
if (data > root.data) {
root.right = insert(root.right, data);
} else {
root.left = insert(root.left, data);
}
return root;
}
}
@Data
class Node {
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
int hrzDis;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
package org.wesome.dsalgo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class BinarySearchTreeTest {
@Test
void testTopViewSingleNode() {
BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();
tree.insert(10);
BinarySearchTree.topView(tree.root);
// Expect output: "10"
}
@Test
void testTopViewBalancedTree() {
BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();
tree.insert(10);
tree.insert(5);
tree.insert(15);
tree.insert(3);
tree.insert(7);
tree.insert(12);
tree.insert(20);
BinarySearchTree.topView(tree.root);
// Expect output: "3 5 10 15 20"
}
@Test
void testTopViewSkewedLeftTree() {
BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();
tree.insert(10);
tree.insert(9);
tree.insert(8);
tree.insert(7);
BinarySearchTree.topView(tree.root);
// Expect output: "7 8 9 10"
}
@Test
void testTopViewSkewedRightTree() {
BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();
tree.insert(10);
tree.insert(11);
tree.insert(12);
tree.insert(13);
BinarySearchTree.topView(tree.root);
// Expect output: "10 11 12 13"
}
@Test
void testTopViewComplexTree() {
BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();
tree.insert(10);
tree.insert(5);
tree.insert(15);
tree.insert(2);
tree.insert(7);
tree.insert(1);
tree.insert(6);
tree.insert(8);
BinarySearchTree.topView(tree.root);
// Expect output: "1 2 5 10 15"
}
@Test
void testTopViewEmptyTree() {
BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();
BinarySearchTree.topView(tree.root);
// Expect output: ""
}
@Test
void testTopViewUnbalancedTree() {
BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();
tree.insert(10);
tree.insert(5);
tree.insert(15);
tree.insert(4);
tree.insert(3);
tree.insert(20);
BinarySearchTree.topView(tree.root);
// Expect output: "3 4 5 10 15 20"
}
@Test
void topViewTest() {
BinarySearchTree binarySearchTree = new BinarySearchTree();
binarySearchTree.insert(4);
binarySearchTree.insert(2);
binarySearchTree.insert(1);
binarySearchTree.insert(3);
binarySearchTree.insert(6);
binarySearchTree.insert(5);
binarySearchTree.insert(7);
BinarySearchTree.topView(binarySearchTree.root);
// Expect output: "1 2 4 6 7"
}
}
plugins {
id("java")
id("io.freefair.lombok") version "8.13"
}
group = "org.wesome.dsalgo"
version = "1.0-SNAPSHOT"
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
testImplementation(platform("org.junit:junit-bom:5.10.0"))
testImplementation("org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter")
}
tasks.test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity is O(n log k), where:
-
nis the number of nodes in the tree. -
kis the number of unique horizontal distances (which is at mostnin a worst-case scenario).
Space Complexity is O(n) for the queue and O(k) for the TreeMap, resulting in a combined complexity of O(n) in the worst case.