The left view of Binary Tree is the set of nodes that are visible when the tree is viewed from the left side. This means that for each level of the tree, only the leftmost node is included in the left view.
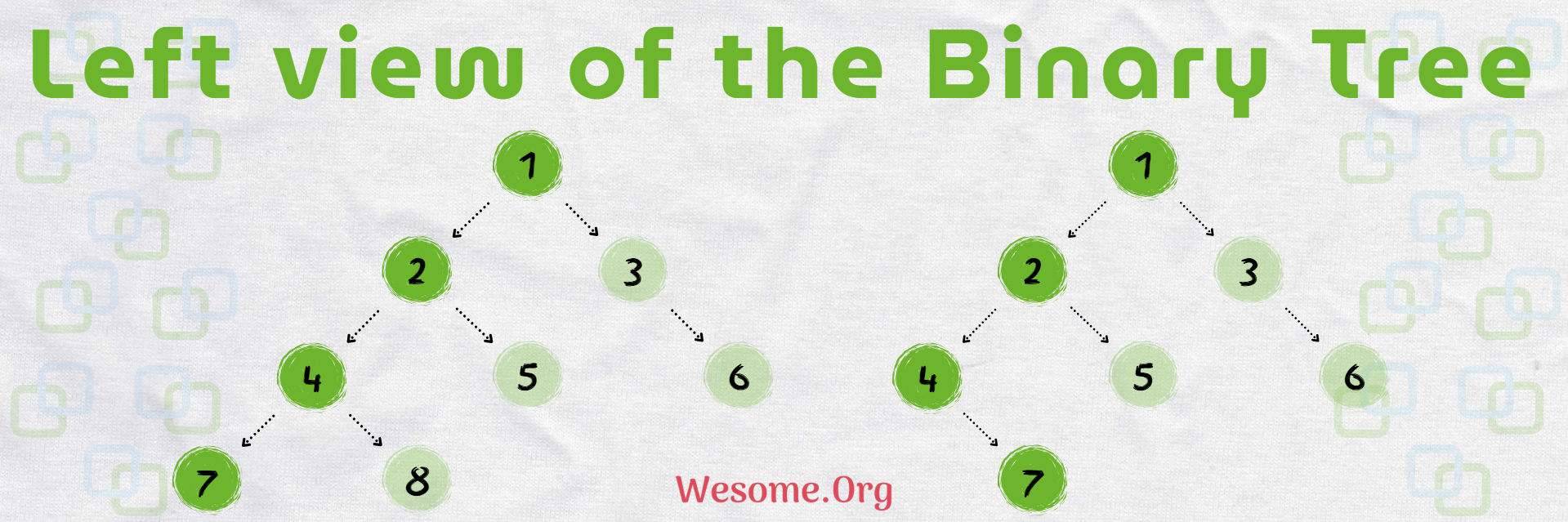
To print the left view of a Binary Tree, we need to display the leftmost node at each level of the tree. This can be done using a level-order traversal also know as Breath First Search with a queue or using preorder traversal also know as Depth First Search with a recursive approach.
The below code is using Level Order Traversal or Breath First Search
Code Flow for Print Left View of Binary Tree
-
Start: Call the leftView(root) method.
-
Check if the root is null:
-
Yes: Exit the method.
-
No: Continue to process.
-
-
Initialize an empty queue and add a root node to it.
-
Loop while the queue is not empty:
-
Get the number of nodes at the current level (size).
-
For each node in the level:
-
Check if it's the first node (i == 1):
-
Yes: Print the node’s data.
-
-
Add the left child (if it exists) to the queue.
-
Add the right child (if it exists) to the queue.
-
-
-
Repeat for all levels of the tree.
-
End.
Let's see the code now
package org.wesome.dsalgo;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Queue;
@Data
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinarySearchTree {
Node root;
public static void leftView(Node root) {
if (Objects.isNull(root)) {
System.out.println("the root is null");
return;
}
/* Uses a level-order traversal approach with a queue. */
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
/* Checks if the root is null and exits if true. */
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
/* Adds the root node to a queue. */
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
Node node = queue.poll();
/* For every level, the first node (i == 1) is printed. */
if (i == 1) {
System.out.print("[" + node.data + "]");
}
if (Objects.nonNull(node.left)) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (Objects.nonNull(node.right)) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
}
}
void insert(int data) {
System.out.println("BinarySearchTree.insert data = " + data);
root = insert(root, data);
}
Node insert(Node root, int data) {
/* If the current root is null, a new node is created and returned. */
if (Objects.isNull(root)) {
Node tempNode = new Node(data);
return tempNode;
}
/* If the data is greater than the current node's value, the method recurses to the right subtree. */
if (data > root.data) {
root.right = insert(root.right, data);
}
/* it recurses to the left subtree. */
else {
root.left = insert(root.left, data);
}
return root;
}
}
package org.wesome.dsalgo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertDoesNotThrow;
public class BinarySearchTreeTest {
@Test
void testNullRoot() {
// Test edge case: Null root (tree is empty)
Node root = null;
assertDoesNotThrow(() -> BinarySearchTree.leftView(root));
// Expect no output
}
@Test
void testSingleNodeTree() {
// Test edge case: Tree with a single node
Node root = new Node(1);
BinarySearchTree.leftView(root);
// Expect output: "1"
}
@Test
void testCompleteBinaryTree() {
// Test case: Complete binary tree
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
BinarySearchTree.leftView(root);
// Expect output: "1 2 4"
}
@Test
void testLeftSkewedTree() {
// Test edge case: Left-skewed tree
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.left.left = new Node(3);
BinarySearchTree.leftView(root);
// Expect output: "1 2 3"
}
@Test
void testRightSkewedTree() {
// Test edge case: Right-skewed tree
Node root = new Node(1);
root.right = new Node(2);
root.right.right = new Node(3);
BinarySearchTree.leftView(root);
// Expect output: "1 2 3"
}
@Test
void testUnevenTree() {
// Test case: Uneven tree structure
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.left.right = new Node(4);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.right.left = new Node(5);
BinarySearchTree.leftView(root);
// Expect output: "1 2 4"
}
/* Binary Search Tree is every node's right subtree contains values greater than the parent node and left subtree contains values less than the parent node */
@Test
void testBinarySearchTest() {
BinarySearchTree binarySearchTree = new BinarySearchTree();
binarySearchTree.insert(1);
binarySearchTree.insert(4);
binarySearchTree.insert(2);
binarySearchTree.insert(3);
binarySearchTree.insert(6);
binarySearchTree.insert(5);
binarySearchTree.insert(7);
binarySearchTree.insert(7);
BinarySearchTree.leftView(binarySearchTree.root);
// Expect output: "1 4 2 3 7"
}
}
plugins {
id("java")
id("io.freefair.lombok") version "8.13"
}
group = "org.wesome.dsalgo"
version = "1.0-SNAPSHOT"
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
testImplementation(platform("org.junit:junit-bom:5.10.0"))
testImplementation("org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter")
}
tasks.test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}Complexity Analysis
- The time complexity is O(N) time since every node is visited once.
- Space Complexity can be O(N) for queue in the worst case.